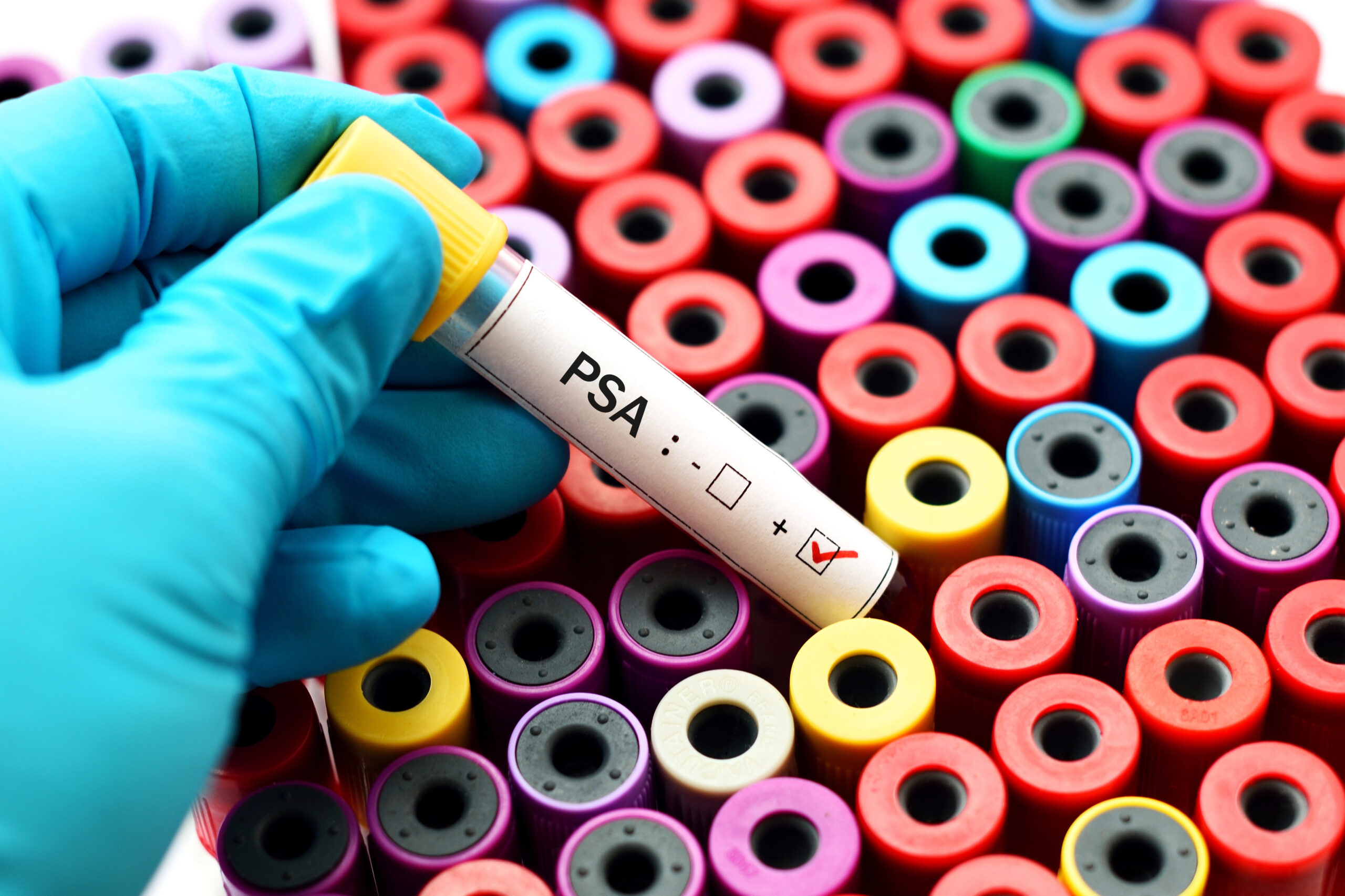
Thinking about scheduling your prostate cancer screening? One way to test for prostate cancer is a prostate-specific antigen level test, also called a PSA blood test.
Here’s common questions surrounding PSA levels and our answers.
Q:
What is an elevated PSA level, and what does it indicate?
A:
An elevated PSA level refers to an increase in the amount of PSA protein present in a man’s blood. PSA is a protein produced by the prostate gland, and its primary function is to liquefy semen.
Q:
What are the potential causes of elevated PSA levels?
A:
Elevated PSA levels can be caused by several factors, including:
1. Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH): BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, which can elevate PSA levels due to increased overall prostate tissue.
2. Prostatitis: Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland, leading to a temporary rise in PSA levels. It is not necessarily indicative of prostate cancer.
3. Prostate Cancer: Elevated PSA levels can sometimes be an early sign of prostate cancer. However, a high PSA level does not confirm cancer, as other non-cancerous conditions can also elevate PSA.
4. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): Infections in the urinary tract or prostate can cause temporary elevations in PSA levels.
5. Prostate Procedures: Certain medical procedures, such as a prostate biopsy or surgery, can cause temporary increases in PSA levels.
Q:
What is the significance of an elevated PSA level regarding prostate cancer?
A:
While an elevated PSA level can be an indicator of prostate cancer, it is not a definitive diagnosis. Many men with elevated PSA levels do not have prostate cancer, and some men with prostate cancer may have normal PSA levels. Therefore, an elevated PSA level requires further investigation to determine the cause. Additional tests, such as a digital rectal exam (DRE) and imaging studies, may be conducted to assess the prostate’s condition and detect any abnormalities.
Q:
At what age should men consider getting their PSA levels checked?
A:
The age at which men should consider getting their PSA levels checked varies based on individual risk factors and guidelines from healthcare organizations. Generally, discussions about prostate cancer screening, including PSA testing, should begin at:
Age 50: For men at average risk of prostate cancer.
Age 45: For men at higher risk, such as African Americans or those with a family history of prostate cancer.
Age 40: For men with a strong family history of prostate cancer (multiple family members diagnosed at a young age).
These are the recommended ages and some factors. Ultimately, the decision to get screened should be made after a thorough discussion with a healthcare provider, taking into account an individual’s medical history, family history, and overall health.
Q:
Can lifestyle factors affect PSA levels?
A:
Yes, certain lifestyle factors can influence PSA levels. Factors such as vigorous exercise, ejaculation, and certain medications (e.g., finasteride) may temporarily elevate PSA levels. It is essential to inform the healthcare provider about any recent lifestyle changes or medication use before undergoing a PSA test to ensure accurate interpretation of the results. However, lifestyle factors do not have a significant impact on PSA levels in the context of diagnosing prostate cancer or other prostate-related conditions.